テキストを呼び出すとき
D1=importdata('qcm.txt')
D1.data(:,1)
により値を制御
1⇒周波数
2⇒実部
3⇒虚部
ZnO Biosensor
2011年4月20日水曜日
2011年4月16日土曜日
2011年3月31日木曜日
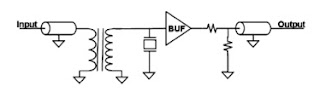
QCM board impedance matching using transformer
To maximize the power that is absorbed by the QCM from the RF amplifier, the impedance of the connection must be as close to the amplifiers impedance (50 Ohms), at resonance, as possible to minimize loss due to the driving signals reflections.
This is achieved using a transformer to match the impedance to the crystal, as shown in Fig. 6. Impedance was found using the Hewlett Packard Network Analyzer’s (HP3589A) impedance function, to measure and match the QCM impedance at resonance to 50 Ohms. It was found that there is a large difference between the impedance of the QCM measured in gas and liquid; and so separate transformers were chosen for a different environment.
Quartz Crystal Microbalance Induced Bond Rupture
Sensing for Medical Diagnostics
M. J. van der Werff, Y. J. Yuan, E. R. Hirst, W. L. Xu, Senior Member, IEEE, H. Chen, and J. E. Bronlun
This is achieved using a transformer to match the impedance to the crystal, as shown in Fig. 6. Impedance was found using the Hewlett Packard Network Analyzer’s (HP3589A) impedance function, to measure and match the QCM impedance at resonance to 50 Ohms. It was found that there is a large difference between the impedance of the QCM measured in gas and liquid; and so separate transformers were chosen for a different environment.
Fig. 6.
Quartz Crystal Microbalance Induced Bond Rupture
Sensing for Medical Diagnostics
M. J. van der Werff, Y. J. Yuan, E. R. Hirst, W. L. Xu, Senior Member, IEEE, H. Chen, and J. E. Bronlun
2011年3月30日水曜日
Mason等価回路
Masonの等価回路を考えるとき、基板および液体の音響インピーダンスの虚数項を含まない場合、共振周波数の変化は全くないことがいえる。
粘性は横波の減衰に大きく関わり、弾性定数の虚部を表すことができる。
損失なしの場合
k=v*sqrt(rou/c)
k:波数
v:音速
rou:密度
c:弾性定数
Z0=rou*v
Z0:音響インピーダンス
損失ありの場合
k=j*w*sqrt(rou/Cr+j*Ci)
Z=sqrt(rou(Cr+j*Ci))
Cr⇒通常の弾性定数
Ci⇒角周波数*粘度
Ztanh(kd/2)
Z/sinh(k*d^2)
登録:
コメント (Atom)